Pest Control and the prevalence of German Cockroaches
In the realm of household pest management, German cockroaches often take center stage due to their persistence and adaptability. However, achieving effective pest control requires a comprehensive understanding of not only German cockroaches but also other prevalent cockroach types. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of cockroaches: starting from German cockroaches to American cockroaches exploring the causes of their prevalence, their habits, the risks they pose, and effective methods for elimination. To help you safeguard your home and family from their menace.
Get A Free Quote
WHAT ARE THE TYPES OF COCKROACHES?
In Sydney, there are various types of cockroaches other than German cockroaches can be found, each with its own unique characteristics and habits. Here are some common types of cockroaches found in Sydney ranking from most common to least
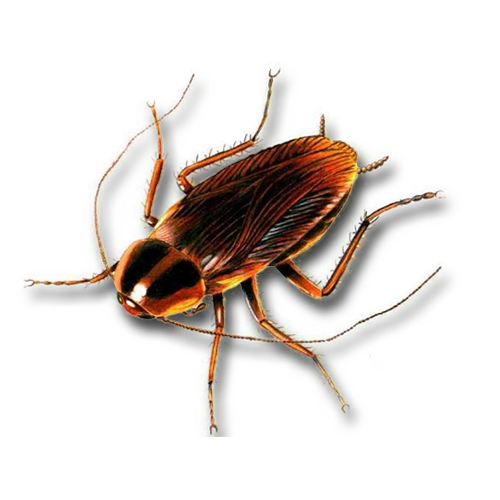

German Cockroaches
Appearance: German cockroaches are small in size (around 1-2 cm long), light brown or tan in color, with two dark stripes on the pronotum.
Habitat: German cockroaches prefer warm, humid environments such as kitchens, bathrooms, and food storage areas. Can also be found in cracks and crevices near water sources.
Behavior: German cockroaches are nocturnal and highly adaptable, capable of rapidly reproducing and establishing large populations within homes.
Threat: German cockroaches are known for transmitting diseases, contaminating food, and triggering allergies and asthma in sensitive individuals.

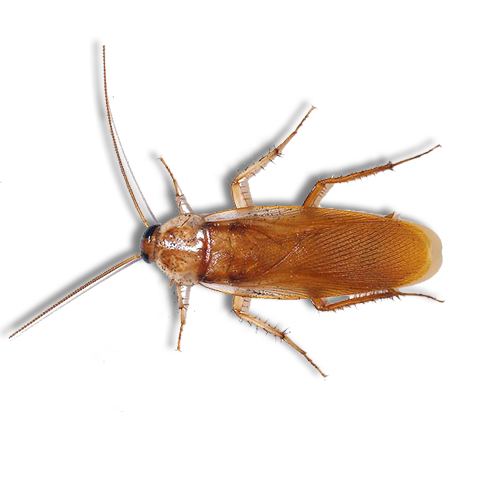
Australian Cockroaches
Appearance: Bigger than German cockroaches, they are medium-sized (around 1 to 1.5 inches long), reddish-brown in color, with distinctive yellow margins on the pronotum.
Habitat: Typically found outdoors in garden areas, mulch, and leaf litter. Can also invade homes, particularly during hot and dry weather.
Behavior: Omnivorous scavenger, feeding on a variety of organic matter. May enter homes in search of food and shelter, particularly in warmer months.
Threat: While less common indoors than German cockroaches, Australian cockroaches can still pose a nuisance and may contaminate food and surfaces.
Shrink

Oriental Cockroaches
Appearance: Medium to large in size (around 1 to 1.25 inches long), shiny black or dark brown in color, with a stout body.
Habitat: Prefers cool, damp environments such as basements, crawl spaces, and drains. Can also be found outdoors in garbage areas and under debris.
Behavior: Nocturnal and sluggish in movement, often found in areas with high moisture levels. Capable of surviving in colder temperatures than other cockroach species.
Threat: While less common indoors than German cockroaches, Oriental cockroaches can still pose a nuisance and may contaminate food and surfaces.
Shrink

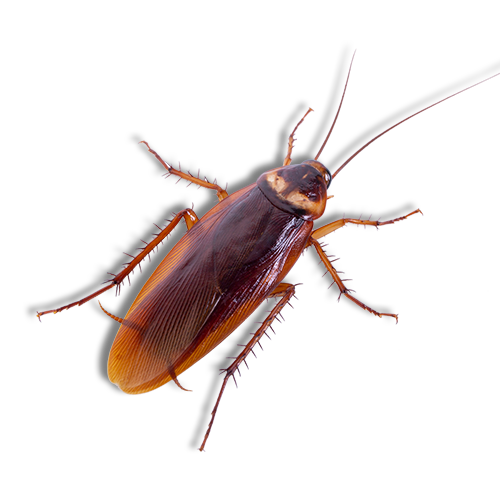
American Cockroaches
Appearance: Large in size (around 1.5 to 2 inches long), reddish-brown in color, with a yellowish figure-eight pattern on the pronotum.
Habitat: Prefers warm, damp environments such as basements, crawl spaces, and sewers. Can also be found outdoors in leaf litter and mulch.
Behavior: Nocturnal and highly mobile, capable of flying short distances. Often enters homes through sewer pipes and drainage systems.
Threat: While less common in Sydney homes compared to german cockroaches species, American cockroaches can still transmit diseases and trigger allergic reactions.
Understanding the characteristics and behaviors of these cockroach species is essential for effective pest control in Sydney homes. It’s essential to identify the type of cockroach infestation to implement targeted control measures.
Feel Free to connect with us
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF COCKROACHES INFESTATION?
Understanding the causes of cockroach infestations in Sydney is crucial for effective pest control especially for german cockroaches. Here are some common factors contributing to the proliferation of cockroaches in the region

Warm Climate
Sydney’s warm and humid climate provides ideal conditions for cockroach breeding and survival. Cockroaches thrive in temperatures between 70°F and 85°F (21°C to 29°C), making the city’s climate conducive to their proliferation throughout the year.

Urbanization and Development
Urbanization and development activities create abundant hiding places and food sources for cockroaches. Construction sites, abandoned buildings, and poorly maintained structures provide ideal harborage sites and breeding grounds for cockroach populations to flourish.

Poor Sanitation Practices
Inadequate sanitation practices contribute significantly to cockroach infestations. Food residues, spills, and crumbs left uncleaned in kitchens, restaurants, and food storage areas attract cockroaches in search of food and water sources.

Leaky Plumbing and Moisture Issues
Inadequate sanitation practices contribute significantly to cockroach infestations. Food residues, spills, and crumbs left uncleaned in kitchens, restaurants, and food storage areas attract cockroaches in search of food and water sources.

Improper Waste Management
Improper waste management practices, such as leaving garbage bins uncovered or overflowing, provide ample food sources for cockroaches. Rotting organic matter, food scraps, and decaying vegetation attract cockroaches and other pests, leading to infestations in outdoor and indoor environments.

Transportation and Migration
Cockroaches can hitchhike on various modes of transportation, including cargo shipments, luggage, and packaging materials. Infested goods transported into Sydney from other regions or countries can introduce new cockroach populations and contribute to the spread of infestations.
Lack of Pest Control Measures
Inadequate implementation of pest control measures, such as regular inspections, sanitation protocols, and pest-proofing efforts, allows cockroach populations to proliferate unchecked. Failure to address early signs of infestation can lead to widespread and persistent cockroach problems.

Resilience and Adaptability
Cockroaches are highly resilient and adaptable pests capable of surviving in diverse environments and conditions. Their ability to develop resistance to pesticides and adapt to changing circumstances makes them challenging to control once established in an area.
WHAT ARE THE HEALTH RISKS COCKROACHES IMPOSE?
As mentioned earlier, cockroaches pose several health risks to humans due to their habits and biology. Here are some of the main health concerns associated with cockroach infestations in depth
Allergies and Asthma
Their droppings, saliva, shed skins, and body parts contain allergenic proteins that can trigger allergic reactions and exacerbate asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. Exposure to these allergens can lead to respiratory issues, such as wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and difficulty breathing.
Disease Transmission
They are known vectors for various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, which can cause diseases in humans. These pathogens can be transmitted through direct contact with cockroach feces, saliva, or body parts, or indirectly through contaminated food, utensils, surfaces, or indoor air. Common diseases associated with cockroaches include salmonellosis, gastroenteritis, dysentery, and food poisoning.
Triggering Asthma and Allergy Symptoms
They have allergens which can exacerbate asthma and allergy symptoms in susceptible individuals, leading to respiratory distress, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness. Prolonged exposure to those allergens can worsen asthma control and increase the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, particularly in children and adults with pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Contamination of Food and Surfaces
They are omnivorous scavengers that feed on a wide range of organic matter, including food scraps, garbage, feces, and decaying matter, especially german cockroaches. As they forage for food, cockroaches can contaminate surfaces, utensils, and food items with pathogens from their bodies and feces, increasing the risk of foodborne illness and gastrointestinal infections.
Skin Irritation and Dermatitis
Contact with their secretions, feces, or shed skins can cause skin irritation, redness, itching, and dermatitis in some individuals. These skin reactions may be more pronounced in individuals with sensitive skin or allergies to cockroach allergens.
HOW TO GET RID OF GERMAN COCKROACHES?
The elimination of cockroaches before its spreading is crucial precisely to german cockroaches as their infestations occur at your house. Eliminating cockroaches, especially german cockroaches requires a multifaceted approach that targets their hiding places, food sources, and breeding sites. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively eliminate cockroaches:
Identify the Species: Determine the type of cockroaches infesting your property it may be German cockroaches, american, etc. to tailor your elimination efforts accordingly.
Thorough Inspection: Conduct a comprehensive inspection of your home or business premises to identify cockroach hiding spots, entry points, and conducive conditions. Focus on areas such as kitchens, bathrooms, basements, and utility rooms.
Sanitation: Maintain strict cleanliness by eliminating food and water sources that attract cockroaches. Clean up spills promptly, store food in airtight containers, and dispose of garbage regularly. Remove clutter and debris to minimize hiding places.
Sealing Entry Points: Seal cracks, gaps, and openings around doors, windows, pipes, and utility lines to prevent cockroaches from entering your property. Use caulking or weather stripping to seal gaps effectively.
Use of Cockroach Baits:
Baits: Place cockroach baits and gels in areas of cockroach activity, such as kitchen cabinets, under sinks, and along baseboards. Baits attract cockroaches and deliver poison that they carry back to their nest, effectively eliminating the colony.
Insecticides: Use residual insecticide sprays or dusts to treat cracks, crevices, and voids where cockroaches hide. Follow label instructions carefully and consider seeking professional assistance for application in hard-to-reach areas.
Natural Remedies: Consider using natural repellents and deterrents such as diatomaceous earth, boric acid, soap & water or essential oils like peppermint or cedar oil. These substances can help repel cockroaches and reduce infestation levels.
Traps: Set up cockroach traps or sticky traps in areas of high cockroach activity to capture and monitor their presence. Dispose of trapped cockroaches promptly.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up: Continuously monitor for signs of cockroach activity and implement follow-up treatments as needed. Repeat sanitation practices and reapply baits or insecticides as directed for long-term control.
Professional Pest Control: If the infestation persists or if you’re dealing with a severe cockroach problem, consider hiring a licensed pest control professional. They have the expertise, tools, and resources to effectively eliminate cockroaches and prevent future infestations.
Conducting professional pest control involves a systematic approach to identifying, treating, and preventing pest infestations. Here’s a step-by-step guide to conducting professional pest control:
Initial Inspection:
Begin with a thorough inspection of the property to identify pest species, nesting sites, entry points, and conducive conditions.
Use specialized tools and techniques to access hidden areas where pests may be present, such as wall voids, crawl spaces, and attics.
Document findings and assess the extent of the infestation to develop an effective treatment plan.
Risk Assessment:Evaluate potential health and safety risks associated with the pest infestation, as well as any environmental concerns.
Consider factors such as the presence of children, pets, sensitive individuals, and nearby water sources when selecting treatment methods.
Treatment Plan Development:
Based on the inspection findings and risk assessment, develop a customized treatment plan tailored to the specific pest species, infestation severity, and property characteristics.
Select appropriate pest control methods, including chemical treatments, baits, traps, exclusion techniques, and sanitation measures.
Implementation of Control Measures:
Execute the treatment plan using professional-grade pest control products and equipment.
Apply pesticides and insecticides safely and according to label instructions to minimize environmental impact and ensure effectiveness.
Implement non-chemical control methods, such as sealing entry points, removing food sources, and modifying habitat conditions, as needed.
Read more about chemical control
Monitoring and Follow-Up:
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of pest control measures through regular inspections and surveillance.
Adjust treatment strategies as necessary based on monitoring results and feedback from property occupants.
Schedule follow-up visits to assess treatment success, address any remaining pest issues, and prevent reinfestation.
Documentation and Reporting:
Maintain detailed records of pest control activities, including inspection reports, treatment plans, product applications, and follow-up assessments.
Provide comprehensive documentation to property owners, managers, and regulatory authorities as required.
Communication and Education:
Communicate effectively with property occupants about pest control procedures, treatment schedules, and preventive measures.
Educate clients about the importance of sanitation, hygiene, and proactive pest management practices to minimize future infestations.
Continuous Improvement:
Stay informed about emerging pest control technologies, regulations, and best practices through ongoing training and professional development.
Continuously evaluate and improve pest control protocols to enhance efficacy, safety, and sustainability.
By following these steps and adhering to industry standards and regulations, pest control professionals can effectively manage pest infestations and protect public health and property.
Feel Free to connect with us
THINGS YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT GERMAN COCKROACHES
- Over 4,000 different species of cockroaches may be found in the world. The most prevalent type of roach among all those species is the German cockroaches.
- The German cockroach is not limited to eating kitchen scraps; it can consume nearly everything, including toothpaste, glue, hair, and soap.
- According to the tongue-twister definition of thigmotropic, German cockroaches like solid objects to come into contact with all four sides of their bodies. This explains why they are usually discovered hidden in small spaces with narrow gaps. German cockroaches can fit into an opening as small as a penny.
- The oothecal, a thick protective covering, is how female cockroaches safeguard their eggs. Forty eggs can be laid in one oothecal by a single female German cockroach. That is a big brood of cockroaches!
- A cockroach’s head is not necessary for survival. German cockroaches breathe through spiracles located along their body’s sides, and they have open circulatory systems. German cockroaches may respond to stimuli for weeks after having their heads severed because of these two facts. Headless German cockroaches may last for weeks without food, but at some point it will become dehydrated and pass away.
- German cockroaches enjoy warm, humid environments. German cockroaches thrive in environments between 85° and 95°F and 90–95% humidity, while they may also survive in typical room conditions. Cockroaches tend to congregate in areas with the highest humidity or temperature, such as under sinks, above refrigerators and other heat-generating appliances, and near water pipes (cold water pipes offer water from condensation, hot water pipes provide warmth).
- German cockroaches congregate in groups. If you overlook an aggregation site, your property can be left with a cockroach mess. However, the fact that German cockroaches congregate may aid in the management of these pests. The brownish “spotting” that cockroaches leave behind indicates their aggregation spots, which are also good places to apply residual pesticides or baits. Spots can serve as a guide to help you with treatment planning.
- Numerous pesticides are detected and avoided by German cockroaches. The majority of pesticide dusts and sprays have some degree of repulsion. Insecticide-treated surfaces that repel cockroaches reduce the likelihood that they will come into touch with the pesticide long enough to absorb a toxic dose. Treat the deep fractures, fissures, and voids within. Cockroaches, even if repellant, will have to come into touch with pesticide residues if there is no untreated harborage for them to flee to.
- The egg shells of German cockroaches are shielded. Before it hatches, female German cockroaches drop the egg case that has been carried for up to a month. Female German cockroaches are less active and prefer to hide in safe spaces such as cracks and crevices while the egg case is carried. This is why it’s crucial to treat deep inside cracks, crevices, and voids when applying residual insecticides, and to plan follow-up treatments in problem areas a few weeks to a month later to control newly-emerged nymphs.
- The least vulnerable insects may withstand insecticide exposure and pass on their “resistance” to their progeny. It’s possible that this resistance is behavioral or physiological, as we recently discovered with cockroach aversion to specific baits. Use mixtures of insecticides or switch out pesticides on a regular basis to avoid control failures.
FUN FACTS ABOUT GERMAN COCKROACHES
some more lighthearted and surprising facts about German cockroaches:
Speedy Runners: German cockroaches can run up to three miles per hour, which might not sound impressive compared to other animals, but relative to their size, it’s quite speedy!
Airborne Navigators: German cockroaches are not only fast runners but also adept fliers. They can glide for short distances, using their wings to navigate obstacles and find new hiding spots.
Musical Talents: Believe it or not, some people keep German cockroaches as pets! In Japan, there’s even a trend of “musical cockroach concerts” where the insects are trained to crawl over musical instruments, creating unique sounds.
Diverse Species: While the German cockroaches (Blattella germanica) is the most common species found in households, there are over 4,000 species of cockroaches worldwide, each with its own unique characteristics and habits.
Ancient Existence: German cockroaches have been around for millions of years, with fossil evidence dating back over 300 million years. They’ve survived multiple mass extinctions and are considered one of the most resilient creatures on Earth.
Space Travelers: German cockroaches have even been to space! In 2007, a study sent German cockroaches aboard the Foton-M bio-satellite to observe their behavior in microgravity conditions. This research helps scientists understand how organisms adapt to space environments.
Cultural Symbolism: In some cultures, German cockroaches are symbols of resilience, survival, and adaptability. While they may be pests to many, they are revered in some societies for their ability to endure harsh conditions and thrive against the odds.
In conclusion, understanding and effectively managing German cockroaches is paramount in any comprehensive pest control strategy. To truly understand German cockroaches, it’s beneficial to compare and contrast them with other cockroach species. While each species has its own unique characteristics and behaviors, studying them collectively provides valuable insights into cockroach biology, ecology, and management strategies.
For instance, comparing German cockroaches with American cockroaches highlights differences in size, habitat preferences, and reproductive rates. Understanding these distinctions helps identify the most effective control methods for each species. This knowledge informs pest control professionals about potential infestation hotspots and preventive measures tailored to specific environments which makes it easier and possible to eliminate infestations of German cockroaches and prevent their spread. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and follow-up are essential to ensure long-term control and minimize the risk of reinfestation. With a proactive approach and a thorough understanding of German cockroaches behavior, individuals and pest control professionals alike can create healthier, pest-free environments for homes, businesses, and communities.
Get A Free Quote
